
In this work several modelling methods are implemented and tested in COMSOL Multiphysics® software for both discs and microrings:ġ) Direct computation of system transmittance (in 2D) to extract the coupling from the resonance curves.Ģ) Partial computation of system transmittance (in 2D) with 4 portsģ) Modal analysis of the cross-section for quasi-analytical approach, similar to Ĥ) Analytical approach with overlap integral calculation

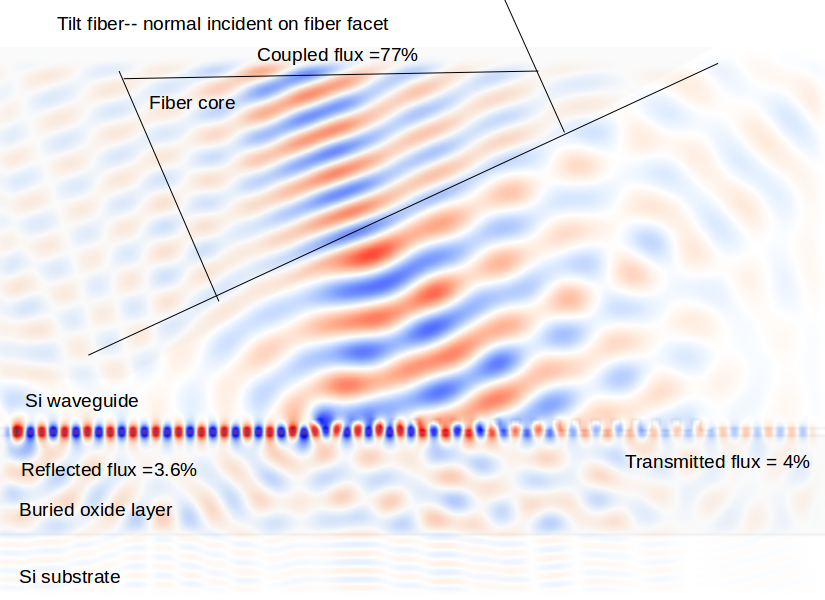
Furthermore, while for big crystalline WGR the coupling can be usually adjusted during experiment, the integral chip resonators are usually fabricated rigidly together with the coupler. The more promissing method, employing waveguides, however, may require careful shape design, requiring numerical modeling. The mos common prism coupler is very robust, but uses free space optics, which is rather bulky. The crucial point in experimental usage of the WGM resonators is coupling to the rest optical cirquit.
They are also widely used in fundamental high-precision experiments like in quantum optomechanics. Many practical applications of such microresonators, such as ultra-sensitive chemical and biological sensors electro-optical modulators, and receivers, optoelectronic oscillators, and optical Kerr comb generators attract growing attention.

Whispering-gallery mode resonators (WGR) are promising elements for future photonic devices, as they combine ultra-high quality factor with small size and mode volume.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
